As you may well know, the digital world is evolving so fast nowadays that it demands, and arguably perhaps even more than ever before, insight into how users behave. To make this happen, Google developed Google Analytics 4, the new data tracking method. Although this method is sometimes referred to as GA4, it is a new technique whereby any business can gain impressive insights into improving its performance based on use. If you’re a newcomer to this platform or changing over from Universal Analytics, here’s your step-by-step playbook to set up and get the most out of GA4.
1. What Is Google Analytics 4?
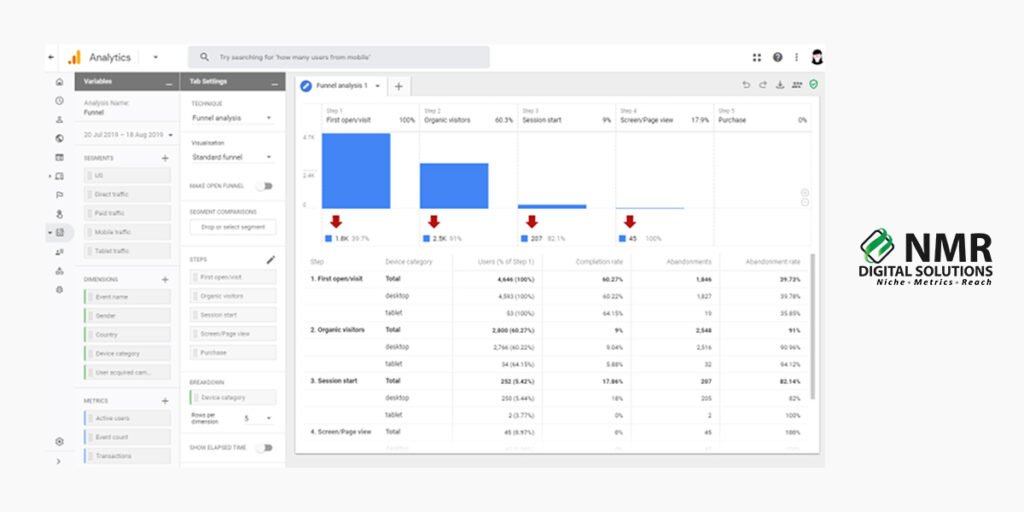
Google Analytics 4 is the latest version of Google’s analytics application, aimed at aiding businesses to track user behaviors across both websites and apps. The older version was almost constructed using Universal Analytics and, whereas that was looking mostly at hitting-based tracking, with most of the focus being laid upon page views, clicks, and so on, the GA4 model is more focused upon its attention to event-based tracking, which makes it way more flexible and perhaps even more detailed with customer interactions.
2. GA4 Setup: Quick Overview
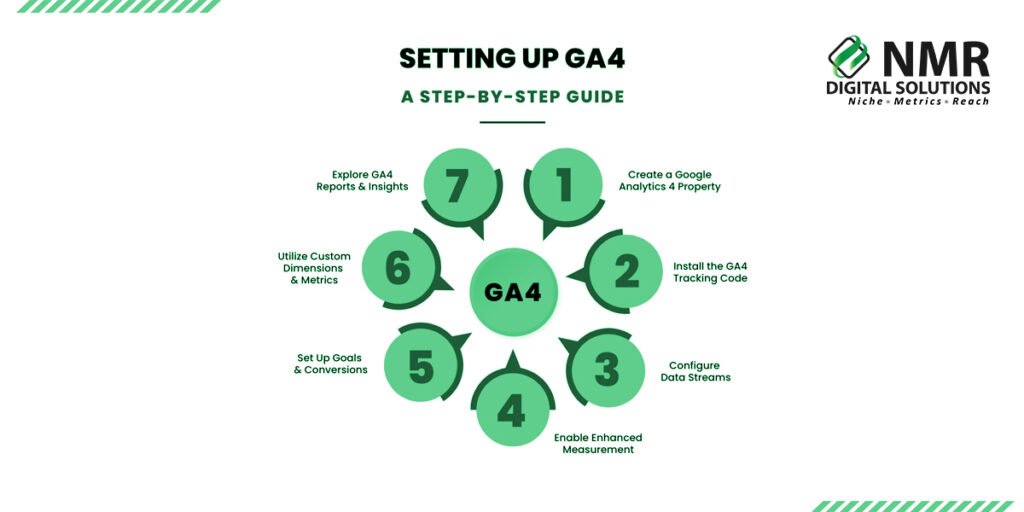
First, you will have to add a new property to your account from Google Analytics 4. But if you already own a Universal Analytics property, then you will also need to configure your new property so you can start tracking parallel data.
To get started,
Log into your Google Analytics dashboard,
click “Admin,” then “Create Property.”
Proceed to Google Analytics 4, and you will follow guided instructions to inject your tracking code effortlessly into your website or application.
As soon as this is done, look for how perfectly all your key events like page views, button clicks, and form submissions are being recorded.
3. Understanding GA4 Metrics
One of the very first differences between GA4 compared to its predecessor is the actual use of organization with data. Instead of sessions and page views, events are actually what guide tracking in GA4. Events are pretty much defined as user interactions, as Google calls them-“events.” These can be a video play to a product purchase.
Metrics are actually what is needed for correct interpretation in GA4. The common metrics are:
Engaged Sessions: This will help in ascertaining how actively users interact with your content.
Event Count: This is the number of events that occurred.
Conversions: It is useful to know how many users completed those desired actions by making purchases or signing up.
4. Tracking User Behavior in GA4
Perhaps one of the strong selling points of GA4 is that it can track user behavior, whether they are or they are not on the website or mobile application, across multiple platforms. This can be quite beneficial for businesses with more than one touch point to analyze where the journey begins.
Critical elements to track:
Page Views: Know which pages have received the most visitors.
Event Tracking: It tracks the specific activities that a user has performed on the website or application, such as button clicks or video views.
Session Duration: It tracks how much time users spend on your website or application.
These metrics do provide a well-informed picture of the engagement of any business and allows it to shift its marketing tactics accordingly.
5. GA4 Event Tracking: Key Features
A tracking system in GA4 is based on events. Unlike Universal Analytics, where tracking was based on session duration and page views, GA4 focuses centrally on events.
You can define events for the following actions-
• Clicks on Buttons
•Form Submissions
•Video Plays
Downloads
These events help you track real-time activities made by visitors with your content.
6. Set up Conversions in GA4
When you enable GA4 conversions, you can track critical actions taken on your website – purchases or sign-ups. To do this, you’ll follow these steps:
Open your Google Analytics 4 dashboard.
Click the “Events” tab under the “Configure” menu
Turn on the toggle next to any event in the list that you want to denote as a conversion.
Conversions help determine how well your campaigns are faring as they provide a direct way of understanding how people are interacting with your website or application.
7. Creating GA4 Custom Reports
Although there are hundreds of default reports in GA4, you probably want to generate some GA4 custom reports relevant to your business needs. With this, you will be able to go into the metrics that you want to notice, and you can also compare your metrics in ways that are very relevant to your strategy.
How to create a customized report:
Open the “Explore” tab in the GA4 dashboard
Choose from hundreds of templates or start fresh
Choose the metrics and dimensions you need
This will enable you to go deep on exactly the data that matters to your business, making decisions so much smarter.
8. GA4 vs Universal Analytics: What are the differences?
If you’re already familiar with Universal Analytics, switching to GA4 may be a bit intimidating. Here are a few important differences:
Event-Based Tracking. GA4 is quite a leap from session-based tracking and shifts towards an event-based model.
Cross-Device Measurement. GA4 integrates seamlessly with the capability of measuring activity across websites and mobile applications, providing companies with an understanding of how users engage.
Privacy First. Measures of GA4 are more stringent than with other analytics solutions, so there is even better compliance with GDPR and other regulations.
Knowing the most relevant differences will make the transition much smoother, and you will be able to take full advantage of using GA4.
9. Data Analysis in GA4
GA4 makes the tool much easier to analyze data as it provides an intuitive interface with robust capabilities. The platform includes visualization tools, such as funnels, path analysis, and user behavior flow charts that allow a company to understand how users navigate to the website or app.
The main GA4 data analysis basics are as follows:
Audience Segments: You can segment your users by their behavior, demographics, or technology usage.
Conversion Paths: GA4 lets you understand where users are going in the buying funnel.
Event Reports: You can get granular insights into what specific user interactions on your platform are occurring.
10. GA4 Tutorials for Beginners
Google has a myriad of GA4 tutorials, starting from beginner level to training for setting up accounts and steps on how to create custom reports. These are very helpful resources because they are hands-on mastering of GA4.
Conclusion
With this Google Analytics 4 beginner’s guide, we have brought you through the critical steps to get started and set up and use GA4 correctly. From how to track user behavior in GA4 to setting up GA4 custom reports and analyzing data, the platform creates unique insights for businesses into how users interact with their content. Being ahead of the game in an information-driven business thus depends much on knowing how GA4 has come to be.
